PEROXIDE FORMING COMPOUNDS
RECIEVING A PEROXIDE FORMER
- Please label the peroxide former with the barcode number, correct date of receipt and open date.
- Please remember to input the barcode number, date of receipt, and open date into EHSA.
- Order Peroxide testing strips for your lab space
the different classes of peroxide formers
CLASS A
Chemicals that can spontaneously form peroxides under normal storage conditions without being exposed to air. These are the most dangerous type of peroxide formers because they have the highest risk of forming explosive peroxides.
CLASS B
Chemicals that can spontaneously form peroxides by prolonged contact with oxygen or with being exposed to air to develop dangerous levels of peroxides. These chemicals are commonly hazardous when concentrated, distilled, or evaporated, as the peroxide crystals that may form are highly explosive.
CLASS C
Chemicals that can readily form highly explosive polymeric peroxides when exposed to air, light, or heat. These materials are particularly hazardous due to their tendency to undergo dangerous polymerization reactions initiated or exacerbated by peroxide formation.
when to dispose of peroxide formers
- CLASS A: SEVERE PEROXIDE HAZARD
- Discard within 3 months of receipt, even if unopened
- CLASS B: CONCENTRATION PEROXIDE HAZARD
- Test for peroxide formation at least every 6 months after opening
- Dispose of after 12 months unless testing for peroxides indicates no peroxides present
- CLASS C: PEROXIDE HAZARD
- Test for peroxide formation at least every 6 months after opening
- Dispose of after 12 months unless testing for peroxides indicates no peroxides present
Examples:
-
Butadiene
-
Isopropyl Ether
-
Divinyl Ether
Examples:
-
Diethyl Ether
-
Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
-
Acetaldehyde
Examples:
-
Acrylic Acid
-
Chlorobutadiene
-
Styrene
COMMON PEROXIDE FORMING FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
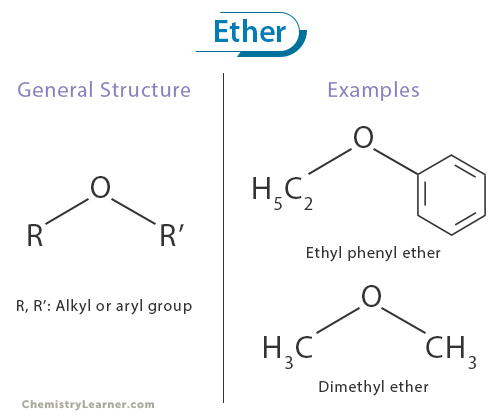
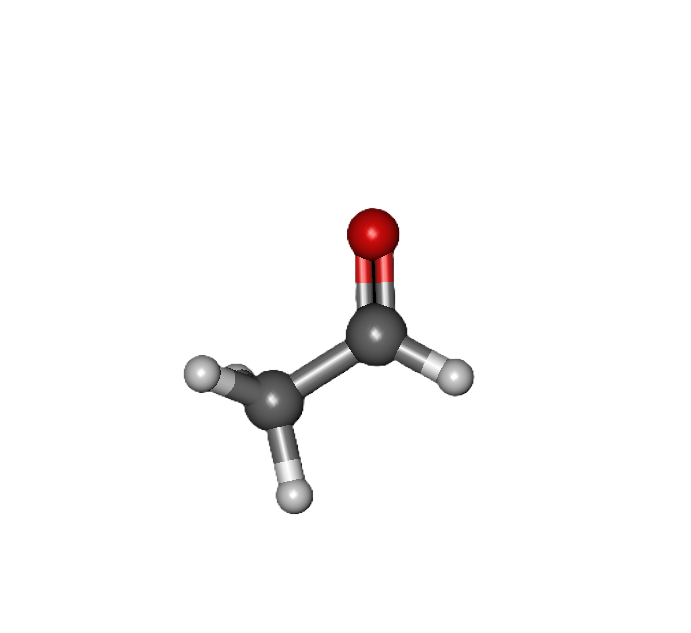
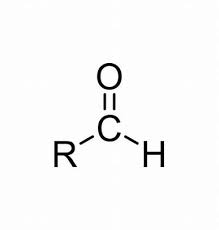
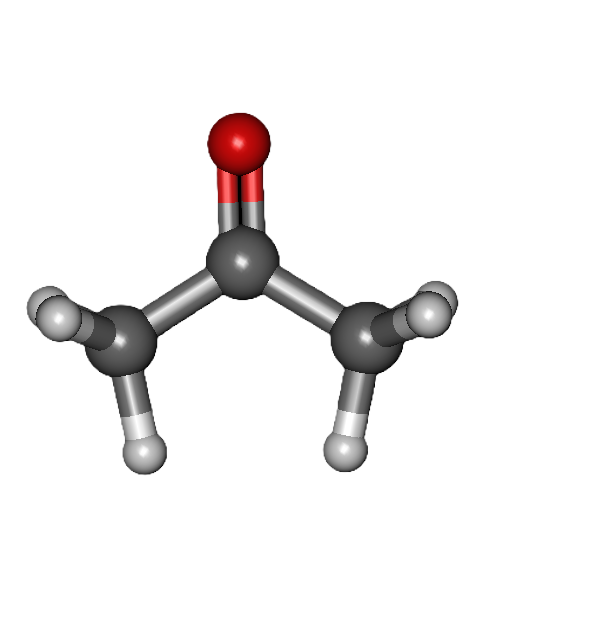
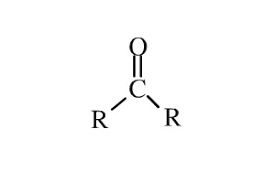
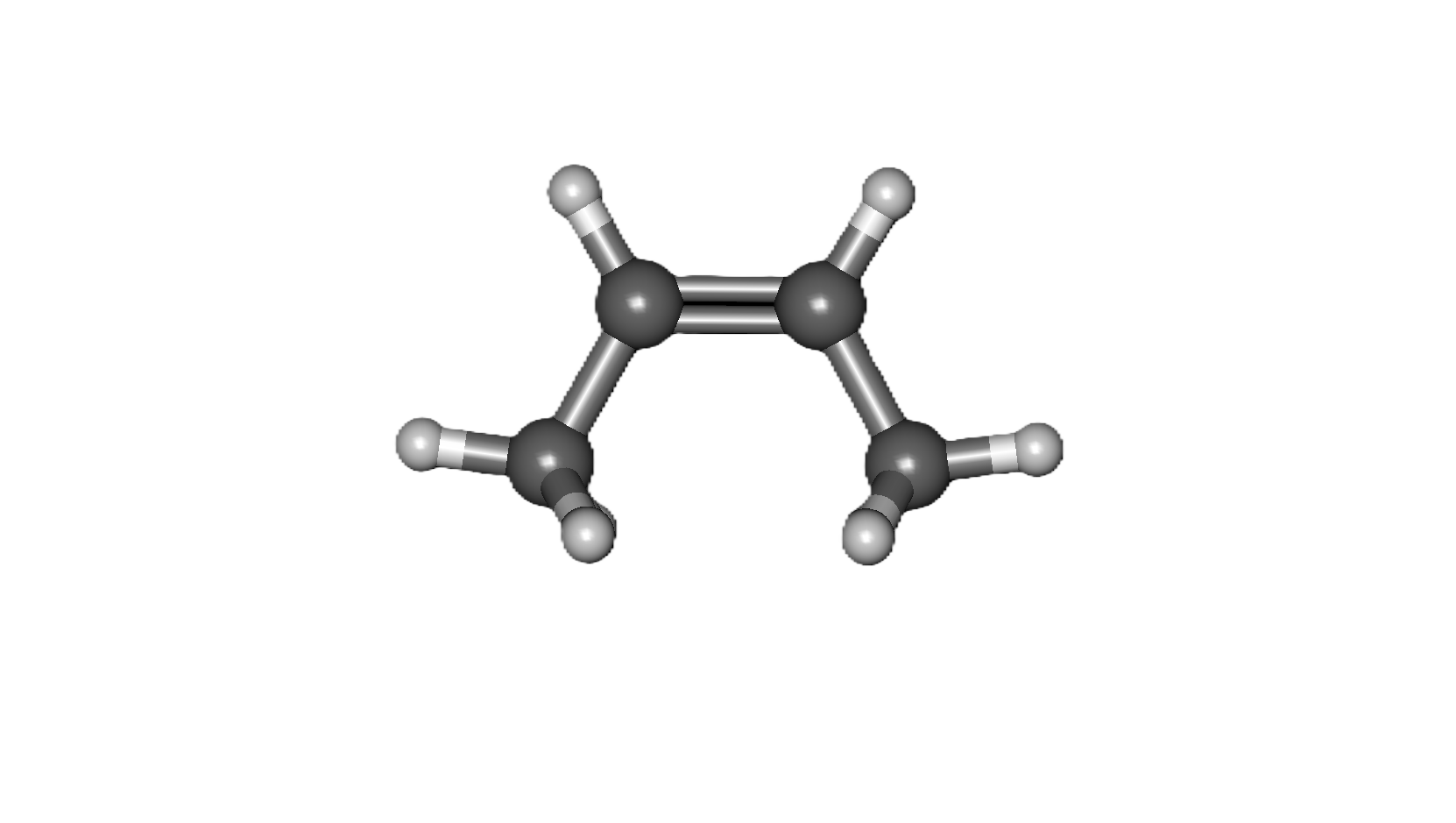
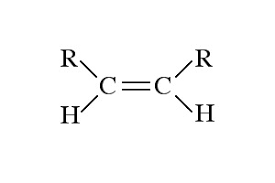
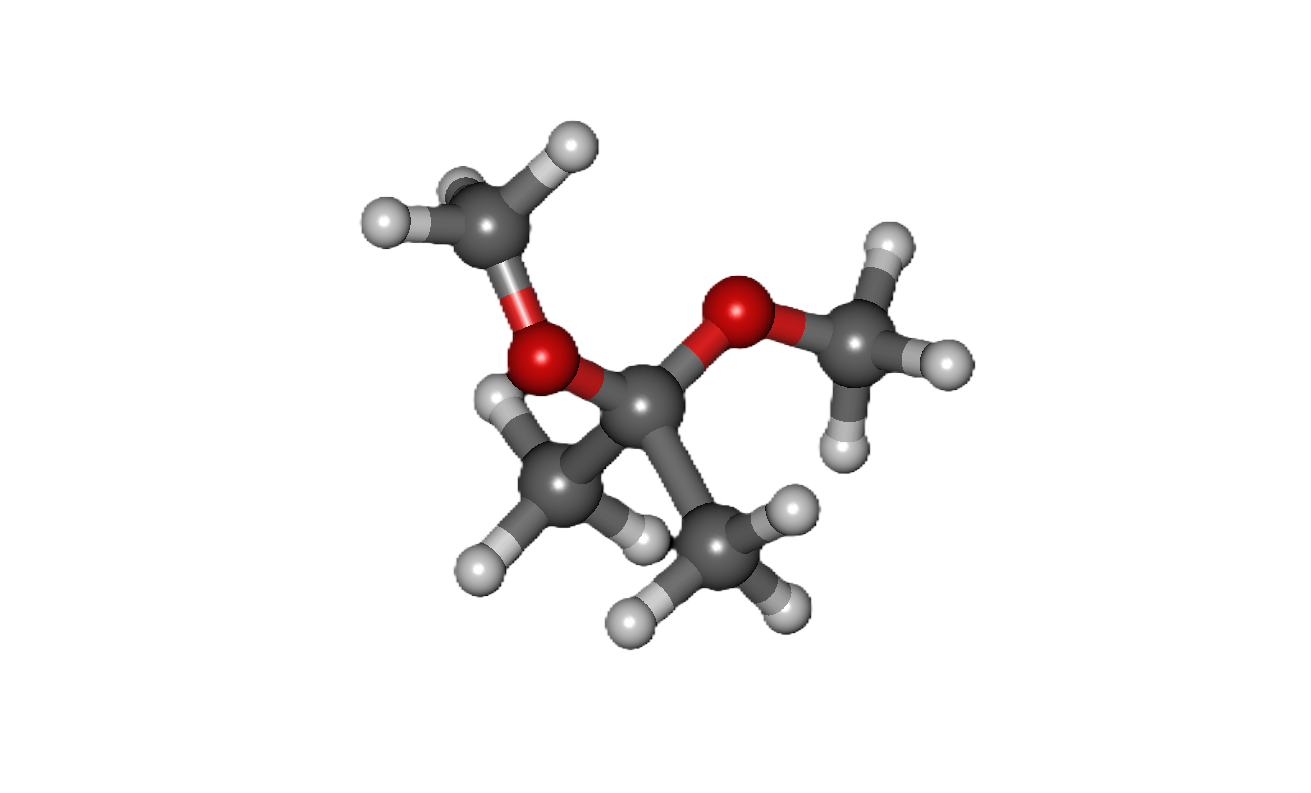
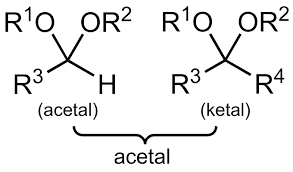
Common Solvents:
Common Solvents: